Asia Map - World's Largest And Most Diverse Continent
With 4 billion people (60 percent of the world's population), Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent. Many of these people live in fantastic landscapes, strange housing, kaleidoscopic traditions, and eat foods that are out of this world.
Author:Michael RachalReviewer:Finn WildeMay 23, 2024216 Shares215.8K Views
With 4 billion people (60 percent of the world's population), Asiais the world's largest and most populous continent. Many of these people live in fantastic landscapes, strange housing, kaleidoscopic traditions, and eat foods that are out of this world.
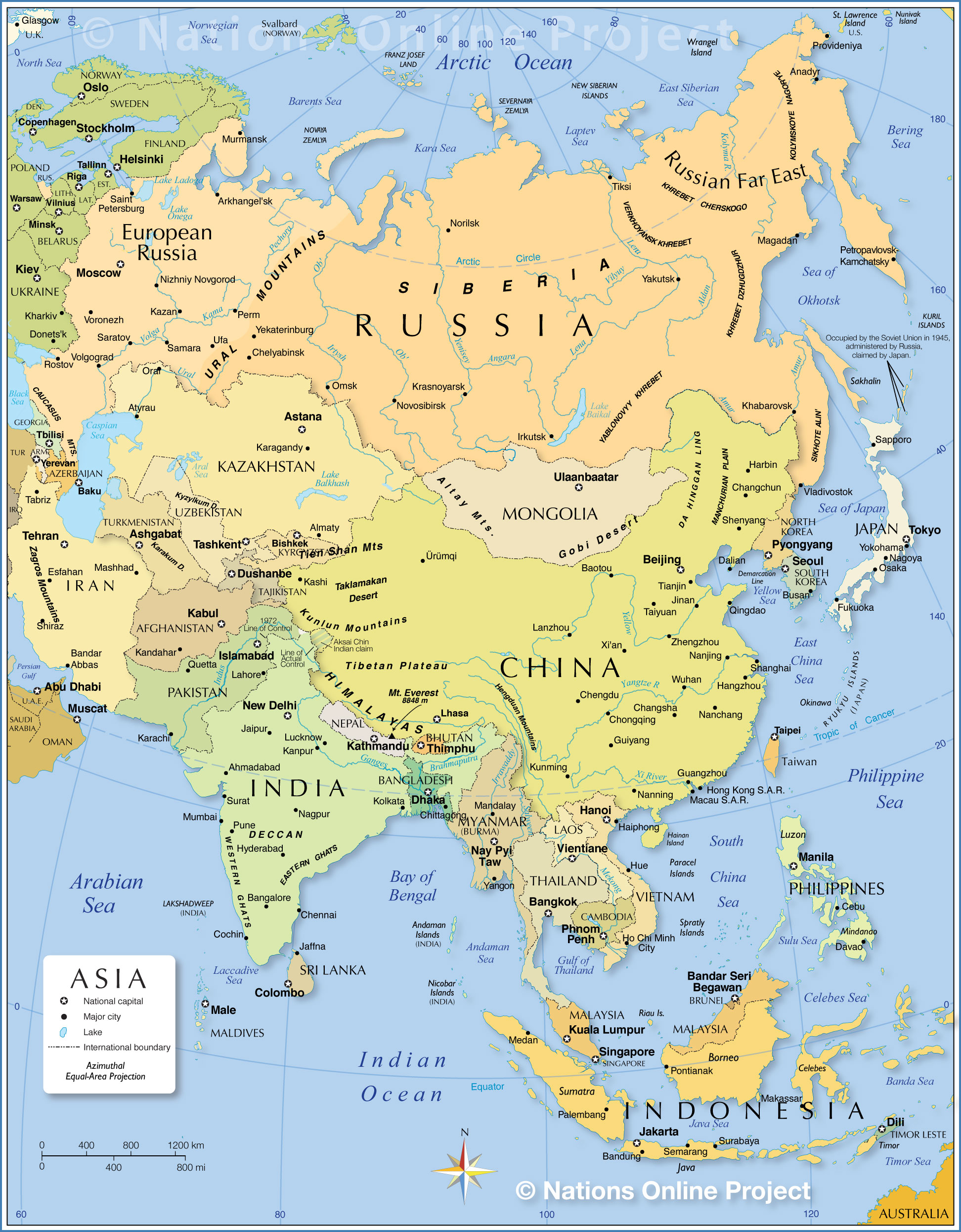
Political Map Of Asia
The Asia mapdisplays Asia without the Middle East. Asia is the world's largest continent, occupying about one-third of the planet's surface and excluding several Southeast Asian islands. Asia dominates Eurasia, the planet's largest landmass. The Malay Archipelago was added to Asia because it is in the area. Asia shares a continent with Europe and is separated by the Ural Mountains and the Caspian Sea. The Arctic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, and Indian Ocean border the continent.
For the average Westerner, Asia means Indian spices, Japanese sushi, Kobe steak, Chinese silk, and fine porcelain. Asia's major religions and philosophies are Zen, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Taoism, despite Indonesiabeing the world's most populous Muslim country.
What Is Asia Famous For?
All of the world's major religions - Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism - as well as numerous lesser ones - were born in Asia.
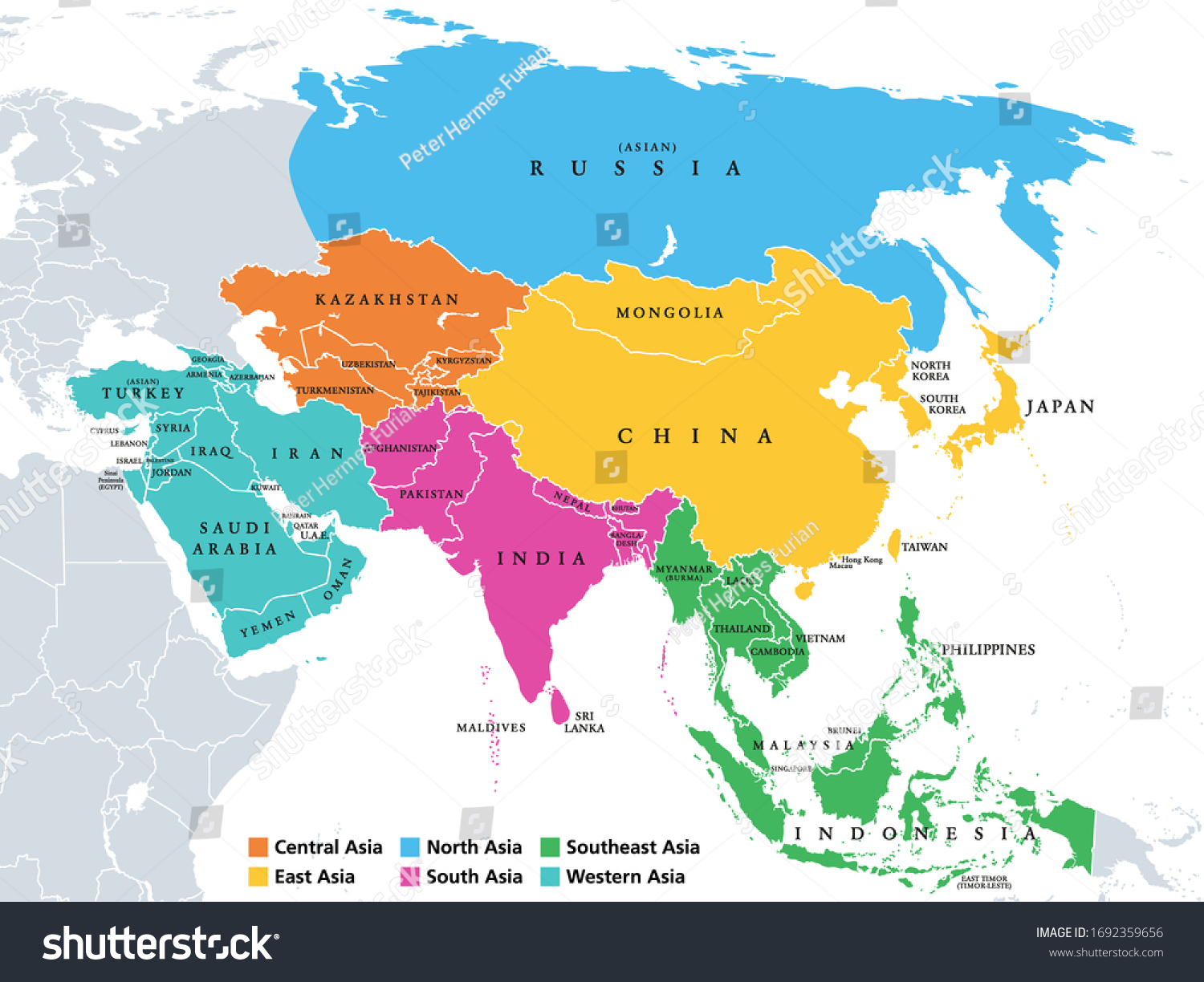
The Diverse Cultures Of Asia
The collective and various practices and traditions of art, architecture, music, literature, lifestyle, philosophy, politics, and religion that have been practiced and perpetuated by the different ethnic groups of Asia throughout prehistory are referred to as Asian culture.
It's difficult to pinpoint a specific Asian culture or universal components among the vast diversity that has emerged from many cultural domains and three of the four ancient river valley civilizations. However, the continent is typically split into six geographic sub-regions that share perceptible characteristics such as culture, religion, language, and ethnic (racial) homogeneity. Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and West Asia are the regions concerned.
Asia, as the world's largest, most populous, and resource-rich continent, is home to some of the world's oldest civilizations, which created the majority of the world's great religious systems, as well as the oldest known documented mythologies and ethics and morality codices.
However, Asia's vast size, immense distances, and inhospitable environments, such as deserts and mountain ranges, separate the numerous civilizations. Trade and commerce eventually evolved a truly international, Pan-Asian character as a result of challenging and overcoming these distances. Inter-regional trade was the driving and unifying force behind the dissemination of cultural components and ideas throughout the large road network and numerous marine links.
China - World's Most Populous Country
In terms of population, China is the most populous country in Asia, with a population rapidly approaching 1.4 billion and a distinct possibility of becoming the world's great superpower in the near future, though India, with its 1 billion people, would argue otherwise. They, as well as their technological prowess, are advancing at a rapid pace in this new world of information technology and outsourcing.
As China becomes a global force, it is critical to comprehend its role and security views of both Asia and the world. Today, China's main concern is domestic political stability. Interfering in China's internal affairs is not welcome. Many Chinese believe the US represents Western culture's essential ideals at odds with China's representation of Eastern civilization. So any American influence is seen as a threat to China's political stability.
Conclusion
A large number of overlapping timelines exist in Asia as a result of the vast landmass and different cultures that exist throughout the region. Another aspect of this is that while each region has a unique history, they all interact in a variety of ways at various moments in time. To get you started, here are some crucial fundamentals to know.

Michael Rachal
Author
Michael Rachal believes that luxury lies in the details. With over 20 years of experience in the luxury travel industry, he has crafted hundreds of bespoke itineraries for clients seeking personalized, unforgettable experiences.
Whether guiding clients through private cultural tours or curating culinary journeys with world-renowned chefs, Michael ensures that each trip is tailored to perfection.
His ability to anticipate needs and exceed expectations has earned him a reputation as a leading expert in luxury travel.

Finn Wilde
Reviewer
For Finn Wilde, the wilderness is more than just a destination - it’s a way of life. Over the past decade, he has led multiple expeditions in some of the world’s most remote regions, from the icy fjords of Greenland to the rugged trails of Patagonia.
Finn emphasizes sustainability in all of his adventures, helping participants connect with nature while promoting responsible exploration. His expeditions inspire individuals to explore the great outdoors while fostering a deep respect for the environment.
Latest Articles
Popular Articles